Page Menu
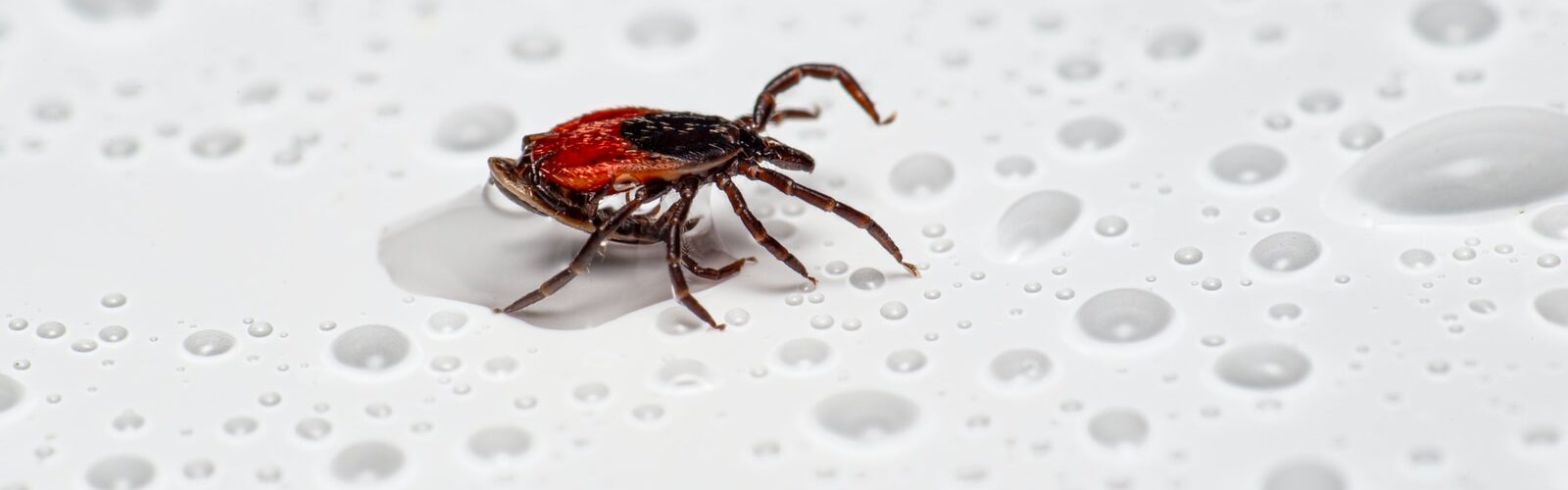
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that can cause severe symptoms, such as fever, rash, and joint pain. There is no cure for Lyme disease, but there are treatments available to help relieve the symptoms. Lyme disease can be caused by exposure to infected ticks, which can be found in forests, fields, and other areas where there are dense concentrations of trees and vegetation. The risk of contracting Lyme disease increases if you are pregnant or have a weakened immune system.
Key Concepts and Top Takeaways
– Be aware of tick habitats: Avoid tall grass and wooded areas during outdoor activities.
– Wear protective clothing: Use long sleeves, pants, and light-colored clothes to spot ticks easily.
– Use insect repellent: Apply EPA-approved repellents containing DEET on exposed skin.
– Perform tick checks: Inspect your body and pets for ticks after spending time outdoors.
– Remove ticks promptly: Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick close to the skin and pull straight out.
– Monitor for symptoms: Watch for fever, rash, or joint pain within weeks of a tick bite.
– Seek medical attention early: Consult a doctor if you suspect Lyme disease symptoms.
– Complete prescribed antibiotics: Follow your healthcare provider's instructions if diagnosed with Lyme disease.
– Educate others about Lyme disease: Share prevention tips with family and friends.
– Stay informed about local outbreaks: Check health department updates on Lyme disease cases in your area.
Please Note: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click one of them, we may receive a commission at no extra cost to you. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

It is most commonly spread in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic United States, but it can also occur in other parts of the world. Lyme disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, including fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. It can also lead to arthritis or other joint problems. In severe cases, Lyme disease can cause serious heart problems or even death. There is no cure for Lyme disease, but there are treatments available that can help relieve symptoms.
If left untreated, Lyme disease can lead to long-term complications such as arthritis and heart problems. There is no cure for Lyme disease, but treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing further infection. Treatment options include antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Prevention involves avoiding tick bites and using insect repellent when outdoors.
Symptoms of Lyme Disease
The most common symptom of Lyme disease is fever, followed by a rash. The second most common symptom of Lyme disease is a rash, usually on the arms or legs, which can be accompanied by fever, headache, muscle aches, stiff neck, and fatigue. Other symptoms may include joint pain, cognitive problems such as memory loss or difficulty concentrating, and seizures. Lyme disease can potentially be diagnosed through blood tests or by reviewing symptoms and history with a doctor. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to clear the infection and relieve symptoms.
Joint pain is a common symptom of Lyme disease. The condition can cause inflammation and pain in the joints, including the neck, shoulders, hips, and knees. In some cases, joint pain may be the only symptoms of Lyme disease. However, joint pain may also be a sign of other health problems, such as arthritis. If you have joint pain and you think you might have Lyme disease, talk to your doctor about your diagnosis.
The symptoms of Lyme disease can be quite varied and can include a wide range of cognitive problems. These problems can be extremely debilitating, and if left untreated, may lead to further complications. It is important that anyone who is experiencing cognitive problems as a symptom of Lyme disease receives proper treatment in order to improve their health and quality of life.
Lyme disease is a relatively new diagnosis that has been on the rise in recent years. Lyme disease is caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria and can be spread through the bites of infected ticks. Symptoms of Lyme disease can include fever, fatigue, headaches, muscle aches and pains, swollen glands, and a rash. Fever is one of the most common symptoms of Lyme disease and can be a sign that the infection is progressing. Lyme disease generally does not require treatment with antibiotics unless it causes serious complications but treating fever can help to reduce its severity and duration.
A headache is one of the most common symptoms of Lyme disease. About 60 percent of people with Lyme disease experience some form of headache. The types of headaches that people with Lyme disease experience can vary, but they usually involve a lot of pain and pressure in the head. Some people also have short-term memory problems and difficulty concentrating.
It can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, neck stiffness, rash, and joint pain. Headache is one common symptom of Lyme disease, and it’s often severe. In fact, about 60 percent of people with Lyme disease experience some form of headache. The types of headaches that people with Lyme disease experience can vary, but they usually involve a lot of pain and pressure in the head.
Lyme disease is a serious infection that can cause muscle aches and other symptoms. Muscle aches can be a sign of the infection and may worsen over time. Lyme Disease is treated with antibiotics, and if treatment is started early enough, most people recover without long-term effects. However, muscle aches can persist even after successful treatment, and may be a sign of another health problem. If you are experiencing muscle pain, see your doctor to determine if it is related to Lyme Disease.
The stiff neck that is a symptom of Lyme disease can be very uncomfortable and may limit daily activities. In some cases, the stiffness may persist even after treatment for Lyme disease has been completed. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms of Lyme disease, as it may be an early sign that the infection has progressed.
Fatigue is a common symptom of Lyme disease, and it can make it difficult to continue with your treatment. If you’re experiencing extreme fatigue, see your doctor for an evaluation. There are a number of possible causes, including the infection itself, the antibiotics you’re taking, and the symptoms you’re experiencing. Depending on the cause, treatments may include rest, pain relief medications, or both.
Causes of Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and can be contracted from the bite of an infected blacklegged tick. The tick can carry the bacterium for weeks or even months before it infects a human. Lyme disease symptoms can vary, but most people experience flu-like symptoms including fever, headache, muscle aches and fatigue.
Lyme disease is most commonly spread in the United States, Europe, and Asia. In the U.S., it is estimated that about 30,000 cases of Lyme Disease are reported each year. About 10-20% of those cases result in long-term symptoms, such as arthritis and chronic fatigue syndrome.
If left untreated, Lyme disease can lead to joint inflammation, facial palsy and even long-term neurological problems like memory loss or paralysis. There is no specific cure for Lyme disease, but early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics is key to preventing serious health complications.
Risk Factors for Lyme Disease
Lyme Disease is a tick-borne infection that can be serious. Here are some key risk factors:
1) Living in an area with high ticks. It is important to remember that there are precautions that can be taken to reduce the risk of contracting this disease. Here are some tips:
-Tick check regularly and remove any ticks you find.
-Avoid being outdoors when ticks are most active, i.e. early morning and late evening hours.
-Use a repellent that contains DEET or Picaridin, if desired.
-Do not share personal items such as towels, sheets, clothing, or tools with others who have not been vaccinated against Lyme Disease.
2) Having a tick bite. There has been a recent increase in Lyme disease cases in the United States, with some experts attributing this to the increasing popularity of hiking and camping. Tick bites can be a risk factor for Lyme disease, as ticks can transmit the bacteria that causes the illness. If you are bitten by a tick, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
3) Being infected with Lyme disease. Infected people are at risk for other infections, which can make the Lyme disease diagnosis more difficult. In fact, being infected with Lyme disease is one of the most common factors that leads to a later diagnosis of Lyme disease.
The National Institutes of Health report that up to 30% of people who are diagnosed with Lyme disease have also been infected with another tick-borne infection, such as babesiosis or ehrlichiosis. This suggests that knowing your exposure history to ticks is important for monitoring your health and preventing future infections.
4) Having a weakened immune system. Having a weakened immune system is a Risk Factor for Lyme Disease and should be taken into consideration when contracting this infection.
5) Having certain medical conditions (such as HIV, cancer, and arthritis). The risk of contracting Lyme disease increases if you have certain medical conditions, including: being in a region where ticks are common, having a weakened immune system, being pregnant, or having a child under the age of 18 years old. If you are worried that you may have contracted Lyme disease, talk to your doctor.
6) Using a lot of the same areas for hiking or biking. Hiking or biking in the outdoors can be a great way to get exercise and enjoy the natural beauty of nature, but it can also be a risky activity for those who are susceptible to Lyme disease. Lyme disease is an infection caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi that is spread mainly via the bite of an infected black-legged tick.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) warns that hiking or biking in areas where Lyme disease is prevalent is a risk factor for getting infected. In fact, according to the CDC, about 30% of people who develop Lyme disease have contracted it while hiking or biking in an area where ticks are known to be present.
If you are concerned about whether hiking or biking in an area where Lyme disease is prevalent might put you at risk, it’s important to talk to your doctor about your specific situation.
7) Smoking cigarettes. Smoking cigarettes is one of the leading risk factors for contracting Lyme disease. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that smoking cigarettes is associated with a 60% increased risk of developing Lyme disease. Smoking also increases the risk of other serious diseases, such as cancer and heart disease, which can be life-threatening.
Studies have found that people who smoke are more likely to contract Lyme disease than nonsmokers. In addition, research has shown that people who smoke are more likely to develop chronic Lyme infection than people who do not smoke.
Lyme disease is a serious infection that can cause significant physical and psychological symptoms. If you are currently smoking cigarettes and you think you may be infected with Lyme disease, it is important to seek medical attention.
Complications From Lyme Disease
Complications from Lyme disease can include a wide range of symptoms, some of which may be minor and go unnoticed, while others can be more serious. Here are some of the most common complications:
1. Joint pain and swelling. This is one of the most common complications, as the infection attacks the joints and surrounding tissues. Swelling may occur in both the joint itself and around nearby muscles. Pain may also increase significantly, making everyday activities difficult to complete.
2. Eye problems. Lyme disease can cause inflammation and scarring in the eyes, which can lead to vision problems such as double vision or blindness. In extreme cases, eye surgery may be required to remove damaged tissue or correct deformities caused by the infection.
3. Neurological complications. In some cases, the infection can lead to long-term neurological problems, including seizures, memory loss and paralysis. Neurological complications from Lyme disease may be difficult to detect early on and can often go undetected for months or even years. If you experience any of the following symptoms, please consult your doctor: unexplained confusion, difficulty speaking or walking, vision changes or seizures.
Lyme disease is a common bacterial infection that is spread through the bites of infected ticks. Neurological complications from Lyme disease can occur anytime after exposure to the bacteria but are most common within the first year after infection. The most common complication is a tick-borne meningitis infection which can cause serious brain damage in adults and children.
Treatment for Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is a serious infection caused by the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Initial symptoms may include a rash, fever, and fatigue. Later stages of the infection may cause joint pain, neurological problems, and even heart arrhythmias. There is no specific treatment for Lyme disease; however, early diagnosis and treatment is essential to recovery. Treatment typically includes antibiotics and other medications depending on the stage of the infection.
Antibiotics are a common treatment for Lyme disease, and are often the first line of defense. There is some evidence that antibiotics may be helpful in treating Lyme disease even if a person has not had an symptoms for several weeks or months. However, antibiotics should only be used if a doctor thinks they are necessary. It is important to remember that antibiotics can’t cure Lyme disease, but they can help relieve symptoms and may shorten the time someone needs to take other treatments.
Medications can be a very effective treatment for Lyme disease. There are several different types of medications that can be used to treat the illness. Some of the most common medications used to treat Lyme disease include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers. Each of these medications has its own specific benefits and drawbacks. It is important to find a medication that will work best for you as it can significantly improve your symptoms.
Common Questions About Lyme Disease
What does Lyme disease do to a person? Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that can cause serious health problems in people. Lyme disease does a lot of different things to a person, including making the person sick, causing pain, making the person have problems with their heart or breathing, and even causing death. Lyme disease is difficult to treat and can be very dangerous if not treated quickly. If you think you may have Lyme disease, it is important to get treatment as soon as possible.
Can Lyme disease completely be cured? Recent advances in antibiotic therapy and prevention have allowed more people to achieve complete remission of the disease. However, Lyme disease can still be quite debilitating and can even result in permanent disability if not treated aggressively. While there is no cure for Lyme disease, currently available treatments provide significant relief for most patients.
What are the 3 stages of Lyme disease? The three stages of Lyme disease are early stage, mid-stage, and late stage. Early-stage symptoms include fever, headache, and muscle pain. Mid-stage symptoms include a skin rash and arthritis. Late stage symptoms include neurological problems such as memory loss and paralysis. There is no cure for Lyme disease, but treatment options are available to manage the infection.
What happens if you go untreated for Lyme disease? The most common way Lyme disease is diagnosed is through a medical exam, such as a CT scan or MRI. If the person has characteristic symptoms, such as fever, rash, and headache, they may be tested for Lyme disease. If the person tests positive for Lyme disease, they will likely be prescribed antibiotics.
If the person does not have any of the typical symptoms of Lyme disease, there are other ways to test for it. One way is to take a blood test that looks for antibodies to Lyme disease. If the person has antibodies to Lyme disease, they may still have the infection but do not have any of the typical symptoms. Another way to test for Lyme disease is through a stool test. This test looks for bacteria in the person’s feces (stool).
Can you have Lyme disease and not know it? Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and can affect any part of the body. The most common symptoms are a rash, fever, and headache, but Lyme disease can also cause joint pain, seizures, and problems with the brain or heart. If left untreated, Lyme disease can spread to other parts of the body and lead to serious health problems. To avoid getting Lyme disease, be sure to check your skin for red marks or erythema after being in areas where ticks are common (such as woods or fields). If you develop symptoms of Lyme disease, see your doctor as soon as possible.
How do you feel when you have Lyme disease? Lyme disease is a very debilitating and often times life-threatening infection contracted from the bite of an infected blacklegged tick. The infection can cause fever, serious headache, body rash, and fatigue. There is no cure for Lyme disease, but it can be treated with antibiotics. Many people who contract Lyme disease experience significant symptoms that dramatically affect their quality of life.
Why is Lyme disease so bad? Lyme disease is a serious infection caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It can be very hard to treat and can cause long-term health problems. Here are some reasons why Lyme disease is so bad:
1. Lyme disease is a major cause of illness and disability in Europe and North America.
2. Lyme disease often spreads quickly through close contact, making it dangerous even for people who don't have symptoms.
3. Lyme disease can lead to serious heart problems, brain infections, and even death.
4. There is no cure for Lyme disease, but there are treatments that can help improve the symptoms of the infection.
5. Prevention is key to avoiding Lyme disease, so everyone should learn how to identify and avoid the ticks that transmit the infection.
How long can a person live with Lyme disease? The disease can affect any part of the body, but most commonly affects the skin, joints, and nervous system. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are crucial for the best possible outcome. While there is no definitive answer to how long someone can live with Lyme disease, most patients experience significant improvement after antibiotic treatment is started. However, complete clearance of the infection is not always possible, and some patients may experience ongoing symptoms for years after they are fully recovered.
Can you live a normal life with Lyme disease? Most people with Lyme disease can continue to lead normal lives. The key is to get treated promptly if you develop any of the more serious symptoms, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
Can Lyme disease cause weight gain? Research suggests that Lyme disease may also cause weight gain. A study published in the journal PLOS One found that people with Lyme disease were more likely to have an increased BMI (body mass index) than those who did not have Lyme disease. The study looked at data from over 1,000 adults who were participating in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The researchers found that 29% of adults with Lyme disease had an increased BMI compared to only 16% of adults without Lyme disease. This suggests that weight gain may be one of the main symptoms of Lyme disease.
Is Lyme Disease fatal? Lyme Disease is a serious bacterial infection that can be deadly if not treated correctly. However, death from Lyme Disease is very rare, and most people who contract the disease will recover without any permanent health problems. There are a few cases where Lyme Disease has led to death, but these are extremely rare.
The majority of people who contract Lyme Disease will experience symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. These symptoms can make it difficult to function normally and can lead to long-term complications if not treated promptly. If you think you may have contracted Lyme Disease, it is important to visit your doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment.
What antibiotics treat Lyme disease? Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that can be caused by the bite of an infected deer tick. Lyme disease can cause a number of symptoms, including fever, headache, rash, and muscle aches. The most common antibiotics used to treat Lyme disease are amoxicillin and ceftriaxone.
Can your body fight Lyme disease on its own? There is some evidence that your body can fight Lyme disease on its own if you receive timely treatment. Here are some tips to help ensure that you get the best possible care:
1. Early diagnosis is key to successful treatment. Prompt treatment means that antibiotics can clear the infection quickly and reduce the risk of long-term health problems.
2. Get vaccinated against Lyme Disease if you are at risk. The best way to protect yourself from this bacterial infection is by getting vaccinated against it! Vaccination offers significant protection against Lyme disease, even if you have been infected before.
Are some people immune to Lyme disease? Some people are more likely to develop symptoms after being bitten by an infected tick than others. These individuals are known as ” Tick-Borne Disease Indicators” or “TBDI's.
Can Lyme disease affect your legs? Lyme disease is a spirochete-caused infection that can affect any part of the body. In particular, Lyme disease can cause inflammation and pain in the joints, muscles, and tendons. However, Lyme disease can also affect other parts of the body (such as the eyes, heart, and nervous system), so it’s important to be aware of its possible symptoms.
Lyme disease is difficult to treat, but early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics can help prevent long-term damage. If you think you may have Lyme disease, talk to your doctor about your symptoms.
Can Lyme disease lay dormant for years? The disease can cause fever, headache, muscle aches and weakness. If left untreated, it can result in joint pain, facial palsy and even seizures. However, Lyme disease may lie dormant for years without causing any symptoms. In fact, up to 30% of people who are infected with Lyme disease don’t show any signs or symptoms for up to 6 months after being infected. This means that it’s important to get tested if you think you may have Lyme disease because even if you don’t have any noticeable symptoms at first, the infection could still be present and potentially deadly.
Does Lyme disease cause anxiety? Lyme disease is a debilitating illness that can cause anxiety, depression and other mental health problems. New research suggests that Lyme disease may cause an increase in anxiety levels and could even lead to longer-term mental health problems. The study, published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, looked at data from more than 2,000 people who contracted Lyme disease between 2010 and 2015. It found that those who were diagnosed with Lyme disease were three times as likely to experience anxiety disorders than those who did not have the infection. The study authors say that their findings suggest that Lyme disease should be added to the list of conditions that can cause anxiety.
Can I drink alcohol with Lyme disease? While there is no definitive answer, some people believe that it is possible to consume small amounts of alcohol while coping with Lyme disease. However, it is important to speak with a doctor before making any decisions about drinking. Alcohol can aggravate the symptoms of Lyme disease, making it harder to fight the infection. Additionally, excessive drinking can also lead to other health problems. If you are struggling with Lyme disease and alcohol consumption, it is best to talk to a doctor first.
What does a Lyme disease flare up feel like? Lyme disease is a serious infection that can cause fatigue, fever, joint pain, and other symptoms. A flare-up of Lyme disease may feel like a different illness altogether. Flare-ups can be very difficult to detect and can last for weeks or even months. If you are experiencing a flare-up of Lyme disease, it's important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
How do you know if you have late-stage Lyme disease? If you have been diagnosed with Lyme disease, you may be wondering how to know if you have late stage Lyme disease. Late-stage Lyme disease is a serious condition that can damage your health if not treated. Here are three signs that indicate you may have late-stage Lyme disease:
1. You experience severe ongoing pain and inflammation anywhere in your body.
2. Your symptoms become more severe and difficult to manage over time.
3. You develop problems with your heart, liver or nervous system.
In conclusion, Lyme disease is a serious condition that can cause a variety of symptoms. It is important to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms so that you can seek treatment if you are infected. There are a number of complications that can occur as a result of Lyme disease, so it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible.

Kevin Collier is a seasoned health writer at Otchut.com, specializing in over-the-counter medicines, common medical ailments, and general health topics. With a background in healthcare and a passion for making medical information accessible, Kevin aims to empower readers with knowledge to make informed health decisions. When he's not writing, he enjoys researching the latest in health trends and advocating for wellness in his community.