Page Menu
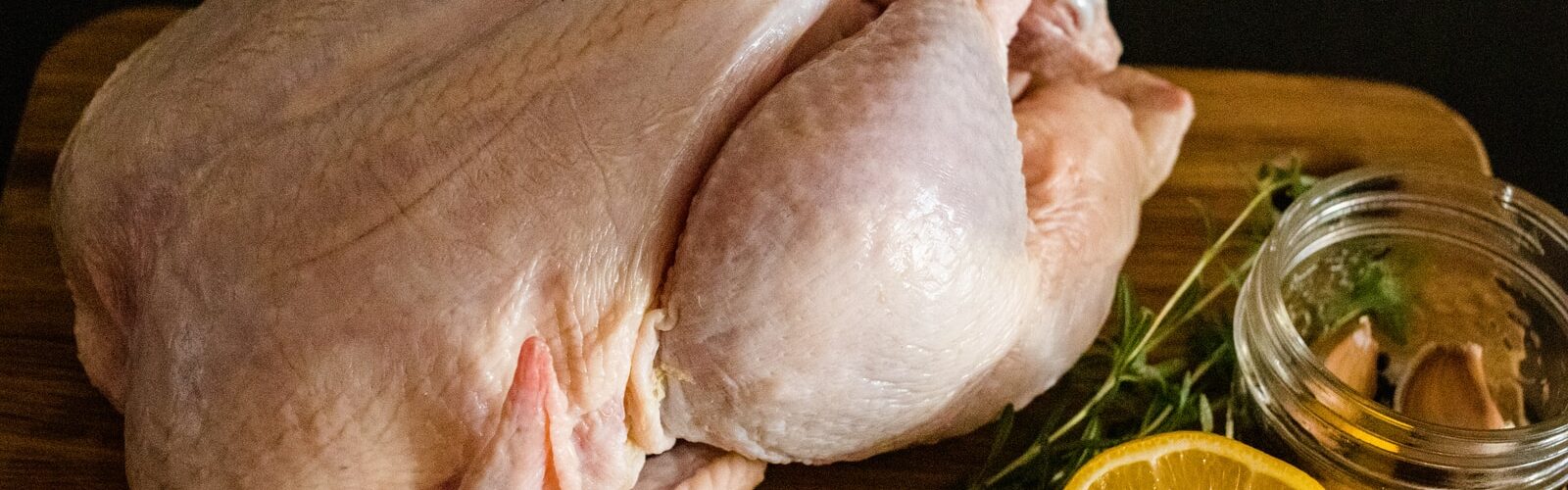
Campylobacter is a bacterial infection that is most commonly found in raw or undercooked chicken. This disease can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, fever, and headache. A person can contract Campylobacter by touching food with their hands after handling uncooked poultry, dogs, cats, or other live animals.
Key Concepts and Top Takeaways
– Practice good hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly before eating and after handling raw meat.
– Cook meat properly: Ensure poultry is cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (75°C).
– Avoid cross-contamination: Use separate cutting boards for raw meat and other foods.
– Drink safe water: Use filtered or bottled water, especially in areas with poor sanitation.
– Be cautious with dairy: Consume only pasteurized milk and dairy products.
– Store food correctly: Refrigerate leftovers promptly to prevent bacterial growth.
– Recognize symptoms early: Watch for diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps after exposure.
– Stay hydrated: Drink fluids to replace lost electrolytes during illness.
– Seek medical help if needed: Contact a healthcare provider for severe symptoms or dehydration.
– Educate yourself about food safety: Stay informed on safe food handling practices to reduce risks.
Please Note: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click one of them, we may receive a commission at no extra cost to you. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

The most common complication of Campylobacter is Guillain-Barré syndrome which can affect the central nervous system due to the destruction of nerve cells.
It is an infection caused by bacteria and is the most common cause of bacterial diarrhea in many countries. It also can be a source of foodborne illness. The symptoms of Campylobacter include stomach pain, diarrhea, fever, nausea, and vomiting. Other symptoms can occur as well, such as muscle aches, headache, or abdominal cramps.
Campylobacter is a bacterium transmitted through food and water. The best protection against contracting Campylobacter is to wash one's hands thoroughly after using the bathroom and before preparing or eating food. If someone does contract campylobacter, they should still be able to enjoy a healthy lifestyle and not suffer complications in the future. Complications may result in IBS, behavioral problems, and even death if not treated with antibiotics.
It can also be found in animal feces and in the environment. It is contracted by eating infected food or drinking contaminated water. Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and cramps. If you have any of these symptoms after consuming potentially contaminated foods, call your doctor immediately or visit the emergency room to assess your risk of having this deadly disease.
It is one of the most common causes of foodborne illness in humans, and it often spread through contaminated poultry meat. In most people, gastrointestinal symptoms will resolve with no long-term consequences, but some may experience reactive arthritis or Guillain-Barré syndrome from Campylobacter's neurotoxin. This disease can be treated with antibiotics; however, severe cases may require hospitalization.
Symptoms of Campylobacter
Campylobacter are bacteria that cause the disease campylobacteriosis. It manifests itself in two main ways, either as a self-limited gastroenteritis or an invasive infection of the bloodstream through the lining of the stomach or intestines. The bacterium can be found in raw poultry, unpasteurized milk, contaminated water, and undercooked meat. Some common symptoms are diarrhea, pain in the abdomen, fever, nausea, vomiting, and sometimes even low white blood cell count.
Campylobacter is a microscopic bacterium that often causes mild to intense nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It can be contracted through a number of ways, one being through raw or undercooked poultry. The first symptom of the infection is generally stomach pain.
The common symptoms of campylobacteriosis, a food-borne bacterial infection, include diarrhea and abdominal cramps. In many cases, these symptoms can be mistaken for a stomach flu or a virus. However, the bacteria that causes the infection is often spread by animal feces, which can contaminate food that has been contaminated with water or soil. One should always take care when handling raw meat to cook it thoroughly and wash any fruits before consumption.
Fever is a common symptom of Campylobacter infection. In the past, medical professionals were unsure whether Campylobacter caused fever in those infected from the bacteria. More recent research has shown this to be true and that a fever may indicate a severe case of the illness.
The term “fever” can be defined as a body temperature consistently higher than 98.
A fever is a common symptom of Campylobacter, leading to 90% of people with it experiencing an elevated temperature. This bacterium is the most common cause of diarrheal illness in the US, which has led many to believe that fever is just an indication of severe illness. The article discusses whether this is the case.
Nausea is a common symptom of Campylobacter, an infection of the intestines. Nausea can be accompanied by feelings of mild to severe distension in the stomach, cramping abdominal pain, and fever. Due to the severity of nausea, it is possible that there could be an underlying issue present, such as appendicitis or gastroenteritis. If you are suffering from these symptoms, please contact your doctor for more information on treatment options.
Nausea is one of the most prevalent symptoms of campylobacter. It is caused by the inflammation in the intestines, which can be very painful. The feeling has been described as similar to the feeling of an early morning hangover. Mild cases may experience nausea only once or twice a day, while more severe cases may experience it for several hours each day.
Campylobacteriosis is a bacterial infection that causes diarrhea, fever, and vomiting. When the illness reaches its third day, it can become chronic and cause problems like muscle pain and arthritis. The bacteria are often found in raw poultry that is not cooked well enough prior to consumption. It can also be found in contaminated water or untreated sewage.
The first symptom for those diagnosed with Campylobacter is muscle aches, which typically occurs 2-5 days after infection. Symptoms such as diarrhea and nausea will also occur during this time period, but it is common for muscle pain to continue long after the other symptoms have ceased.
It’s possible that muscle aches can be the only sign of Campylobacter, and these aches may last anywhere from one to eight weeks.
Campylobacter is a low-risk bacterial infection that can cause people to experience a variety of symptoms including stomach cramps, diarrhea and vomiting. A rare, but serious complication for this illness is headache. People with headache as a symptom should seek medical attention immediately because it can be caused by other things such as skull fracture.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that can be found in raw and undercooked meats. Campylobacter infections typically result in flu-like symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. It can also lead to serious liver complications like Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS). The type of infection and its severity depend on the person’s age and underlying health. Young children and seniors are more likely to suffer from severe complications.
Infection from campylobacter is an intestinal disease caused by eating raw or undercooked poultry. This infection can sometimes cause diarrhea. In some cases, a low white blood cell count may be a symptom of campylobacter. A low white blood cell count is often not something that people know to check for because it does not always occur in those who have been infected with campylobacter.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that is the cause of many symptoms, such as fever, headache, nausea, and vomiting. One of these symptoms is an abnormally low white blood cell count. This article will explore the link between Campylobacter and low white blood cell count.
It is not uncommon for a person with Campylobacter to also suffer from a low white blood cell count. This, in turn, can contribute to an increased susceptibility to infection and illness. Low white blood cells can be found in all parts of the body and are tasked with fighting off infection and disease.
Causes of Campylobacter
Campylobacter is a bacterium that causes gastrointestinal illness in people who consume foods contaminated with these bacteria. Campylobacter infection can cause fever, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, the infection could lead to long-term health problems such as irritable bowel syndrome or reactive arthritis. Campylobacter is transmitted through contact with infected animals or their droppings.
Campylobacter is a common cause of diarrhea. Campylobacter can be transmitted by contact with contaminated food or water, or by coming in contact with an infected animal. The bacteria enter the body through the mouth and can live in a person's intestines for up to a month without causing any problems. Eventually, they may cause a diarrheal illness from 10 to 20 days after becoming infected.
Campylobacter is an infectious bacterial disease that is usually transmitted by tainted poultry. The most common symptom of Campylobacter is diarrhea. Additional symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and malaise. Campylobacter is diagnosed by stool culture on agar plates containing urea and tellurium; if present in the stool, colonies will show after incubation at 44 degrees Celsius for 24 hours.
Risk Factors for Campylobacter
Most people who develop Campylobacter food poisoning will only suffer mild symptoms, such as diarrhea and fever. However, some cases can be much more serious and even lead to death. These high-risk individuals should be aware of the risk factors for Campylobacter and take the appropriate precautions to reduce their chance of infection.
Campylobacter is one of the most common causes of diarrheal illness in developing countries. It was first detected in 1880 and has been present on all continents except Antarctica. The bacterium can be transferred to humans through contact with infected animals or contaminated food. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting that last for 4–7 days on average. Treatments include supportive care and antibiotics to reduce symptoms and shorten the infection's duration.
Many people carry Campylobacter bacteria in their intestines without experiencing any adverse effects. When the bacteria are able to enter the body, they usually do not cause illness. However, when these bacteria enter the body and invade the tissues lining the intestines or other parts of the digestive tract, they can lead to an infection.
Complications From Campylobacter
Campylobacter is a bacterium found in raw or undercooked chicken and unpasteurized milk and juice and other foods. Symptoms of campylobacter infection include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever. While most people recover within a few days without treatment, it can be serious for those with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, those being treated with chemotherapy, those being treated for cancer or autoimmune disorders, as well as young children or the elderly.
Campylobacter is a common strain of bacteria found in raw or undercooked poultry. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has ranked Campylobacter as the leading cause of enteritis, a type of food poisoning, in the United States. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever and vomiting. In severe cases, it can lead to kidney failure or death from sepsis.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that is commonly found in contaminated water sources and raw animal meat. It can be contracted by ingestion, ingestion of contaminated water, inhalation, or contact with the bacteria’s fecal matter. All warm-blooded animals are vulnerable to infection by Campylobacter. The symptoms of Campylobacter include diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, muscle aches, and swelling of the lymph nodes.
The stomach pain most people associate with a case of campylobacter is usually the result of induction from diarrhea, or an inflammation in the intestinal walls. However, for an unlucky few, this may be a complication from campylobacter disease. In some cases, stomach pain can be a sign of a more severe complication, such as peritonitis or acute ileitis.
Campylobacter – a bacterium – is the most common cause for food poisoning. Campylobacter can be found in raw and under cooked chicken and other poultry, unpasteurized milk and dairy products, and untreated water sources (taps). Campylobacter can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever, muscle aches, weight loss, headaches, cramping etc.
The most common cause of the infection is the Campylobacter bacterium, which can contaminate food and water, as well as travel through direct contact with people. Campylobacter is normally not life-threatening, but it can lead to diarrhea if left untreated. It's important to know the signs and symptoms of Campylobacter, so you can properly treat yourself or others with it.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that causes diarrhea in around 10% of patients. These symptoms are often the result of food poisoning due to cross-contamination. However, some people experience chronic bouts of diarrhea without any other explanation. If the symptoms are not controlled, then it may lead to dehydration and weight loss.
Many of the complications from Campylobacter, a foodborne disease, come from fever. Fever can be a complication from the bacteria infection itself or from another cause of illness. For example, fever is often a sign of a urinary tract infection or an infection in the blood.
Infections from Campylobacter are on the rise, and fever is a complication of those infections. The bacteria are found in raw, unpasteurized milk and contaminated water or food. It can be spread through contact with infected animals or people who have not practiced good hygiene. A person with a campylobacter infection may experience symptoms such as diarrhea, stomach cramps, vomiting, fever, and muscle aches.
Many people will experience fever after contracting Campylobacter. It is estimated that 3% of the population will get fever after infection with these bacteria. Fever, or pyrexia, can be defined as an elevation in body temperature to at least 100 degrees Fahrenheit (37.8 degrees Celsius). Fever has many causes, both serious and benign.
Campylobacter is a bacterial infection that can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, stomach pain, and fever. Recently, a study looked at the impact of Campylobacter on headaches in children. They found that headache is a common complication from Campylobacter and recommended patients should be monitored for headache symptoms.
Campylobacter is a common bacterium found in the intestines of mammals, birds, and poultry which can be transferred to humans through contact with an animal's feces. The infection often manifests as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, fever, vomiting, and headache. Headache is one of the most common side effects of Campylobacter.
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a disorder of the peripheral nervous system characterized by tingling or numbness in the extremities, muscle weakness, and, in some cases, paralysis. This syndrome has been linked to Campylobacter jejuni bacteria found in poultry and unpasteurized dairy products.
Guillain-Barré syndrome is an immune system disorder that occurs when the body’s defense mechanisms attack its own nerve cells and causes paralysis. Campylobacter has been recently associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome and this article will explore one possible pathway by which Campylobacter could cause Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Campylobacter is a bacterial infection that can cause severe gastrointestinal issues, including diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain. It has also been shown to trigger irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in some patients. Known as one of the most common causes of infectious diarrheal disease worldwide, Campylobacter affects millions of people each year. This includes many children. The severity of IBS can vary from person to person and includes constipation or diarrhea.
A recent study has found that 34% of patients with IBS experience symptoms immediately following an infection with Campylobacter, an organism that causes gastroenteritis. This complication can lead to long-term and chronic gastrointestinal problems and is also more commonly seen in females than males. Mood disorders such as anxiety and depression are more likely to develop after a Campylobacter infection.
IBS is a chronic disorder that affects people's quality of life. IBS can be investigated to determine if bacteria, such as Campylobacter, are the cause. The stomach and intestines will often show inflammation, and an infection with Campylobacter may contribute to this. Many people suffer from IBS that is caused by a bacterial infection, which could easily be treated with antibiotics.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that can cause behavioral problems in people with certain levels of the bacteria. One of the major areas of concern is the behavior and mental health of children. Adults with severe cases can experience depression, confusion, and even dementia. The most likely way for one to become infected is through the consumption of raw or undercooked poultry.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of reports of adverse health effects related to Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. One such complication is behavioral problems. These include hyperactivity, irritability, and nervousness. Currently, there is no specific treatment for these reactions to Campylobacter infection, but studies are being done on the subject.
Death is often a complication of campylobacteriosis. This type of infection is caused by the bacteria, campylobacter, which lives in contaminated food and water. Symptoms of this infection can include diarrhea, stomach pain, fever, headache, nausea/vomiting and muscle aches. These symptoms usually appear one to four days after consuming the bacteria.
Mortality rates for children around the world are around 50%.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that causes diarrhea and vomiting in humans. Campylobacter is found in both wild and domestic animals and can contaminate food or water sources. If left untreated, the symptoms of campylobacter may take up to two weeks to resolve and can lead to long-term complications such as Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Treatment for Campylobacter
Campylobacter is a bacterium that causes food poisoning through the consumption of raw or undercooked chicken, contaminated water, or contact with infected poultry. The symptoms are typically diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, headache, fever and muscle aches. Effective treatment for Campylobacter involves antibiotics, which are usually given for at least 2 to 3 days' time.
Campylobacter is an incredibly common food-borne illness. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that over 850 thousand illnesses are reported each year in the United States alone.
Some doctors prescribe antibiotics as a treatment for Campylobacter. Antibiotics are able to kill bacteria, but they do not work on viruses, fungi, or parasites. Patients who have been prescribed antibiotics should take them as prescribed and finish all doses.
Campylobacter is one of the most common causes of food poisoning, more than 1 million people get sick each year which lead to about 16 deaths. A lot of research has been done on different types of treatments, but it is hard to find something that will keep you from passing it on to other people. The only real prevention for this is to avoid undercooked food.
Campylobacter, a leading cause of acute diarrhea in the U.S., is often associated with food products. Given the prevalence of this disease, it is important to know about alternative treatments, which are more natural ways of treating Campylobacter without the use of antibiotics. One option is taking probiotics, which are bacteria that can help your gut flora get back to normal without side effects.
Common Questions About Campylobacter
Throughout the summer, many families enjoy going camping and hiking. However, these trips can cause unpleasant stomach problems. Campylobacter is a bacterial infection that commonly causes diarrhea, cramping, nausea, and vomiting. In fact, it can affect as many as three out of four people who go camping or spend time in the wilderness. This being said, those with Campylobacter should avoid drinking untreated water from lakes or rivers because this could potentially spread the infection to others.
Campylobacter is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps. It's commonly transmitted through animal feces or infected food. Campylobacter is the most common cause of foodborne illness in the United States. The U.S. National Library of Medicine estimates 8 million cases yearly, with over 100 deaths annually. This article will discuss common questions about Campylobacter to help you better understand this type of bacteria.
How do you get infected with Campylobacter? 75% of the world’s population is exposed to Campylobacter. This bacterium can be found in contaminated water, undercooked chicken, and unpasteurized milk. If a person eats food with Campylobacter or drinks tainted water that has been contaminated by this bacterium, then they can get infected. One of the main symptoms of Campylobacter infection is diarrhea, which can range from mild to severe.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that causes foodborne illness. It is found in raw or undercooked chicken, unpasteurized milk, untreated water, and untreated fruit juices. Most cases are spread via contaminated food or water. This article explores how the bacteria spreads to humans, preventative measures you can take to stay healthy if you do get infected, and more about the symptoms of Campylobacter infection.
What are the symptoms of Campylobacter? Campylobacter is a bacterium that causes gastroenteritis and appears in coastal and freshwater environments. There are two types of Campylobacters: Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Symptoms of Campylobacter include fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, headache, muscle pain and a stiff neck. In addition to these symptoms, some people may also experience a discharge from the eyes or nose.
There are two common symptoms associated with Campylobacter, diarrhea and cramping. Campylobacter is a bacterium that is found in raw poultry, unpasteurized milk, or contaminated water. The most common way to receive the disease is through consuming raw or undercooked chicken. Symptoms usually appear two days after being infected and last for 7-10 days. If you have diarrhea for more than 3 weeks without relief, consult your doctor right away.
How long does it take to get over Campylobacter? Campylobacter is a bacterium that is responsible for the infection known as campylobacteriosis. It is the most common bacterial foodborne disease in developed countries and usually resolves on its own but can sometimes lead to life-threatening health complications. The symptoms include diarrhea, cramping, abdominal pain, fever, nausea and vomiting. Symptoms usually last 5-7 days and there are no long-term side effects.
The “gastroenteritis” caused by Campylobacter bacterium can last anywhere from 7 to 10 days, but treatments for the bacterial infection are readily available. The bacteria are most commonly found in undercooked poultry, unpasteurized milk and water, and contaminated produce.
Can Campylobacter keep coming back? Campylobacter is a type of bacteria that can be transferred through bad hygiene, or sometimes even food. Campylobacter can make people sick for up to 3 weeks with symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, and fever. It is one of the leading causes of infectious diarrhea in the United States. Currently, Campylobacter may seem like a rare illness, but it can actually come back if untreated.
Campylobacter is a type of bacteria that can cause chronic diarrhea and fever. It is commonly found in raw poultry and unpasteurized milk but can also be found in untreated water sources like lakes and rivers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that Campylobacter affects 2.4 million people each year in the United States, but almost 80% of those infections are asymptomatic.
What should I eat if I have campylobacter? Campylobacter is a type of bacteria that can infect the intestine and cause diarrhea, stomach pain, and fever. The intestinal infection caused by Campylobacter is called campylobacteriosis. Although most people with the infection fully recover without treatment, it may be possible to prevent or lessen your symptoms by changing your diet.
Campylobacter is an infectious bacterium that causes diarrhea, vomiting, and pain in the abdominal area. To avoid getting it, cook food thoroughly and wash your hands after using the bathroom. For those who do develop symptoms, there are several ways to treat it. In addition to taking over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or loperamide for diarrhea, doctors often recommend a probiotic to help build up good bacteria in the gut.
Can campylobacter go away on its own? In the United States, Campylobacter is a common cause of bacterial foodborne illness. In 2015, for instance, over 1.3 million cases were reported. Many people believe that these bacteria can go away on their own, but this is not true. The Center for Disease Control recommends taking antibiotics to treat the infection and doing so as soon as possible after becoming aware of it. This will help shorten how long you have the symptoms and reduce the chances of spreading it to others.
Campylobacter is a germ that can cause bloody diarrhea, fever, stomach cramps, and nausea. Many people have heard that campylobacter can go away on its own within a few days to a few weeks. However, this isn’t always the case, as some people need medical treatment for their symptoms until they feel better.
How do you diagnose Campylobacter? Campylobacter is a bacterium that causes diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps. It can be treated with antibiotics but is often misdiagnosed because it is highly contagious. In order to diagnose Campylobacter, the doctor will take a stool sample from the patient and send it to a lab for testing. If the lab results come back positive for Campylobacter, then the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Campylobacter can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms are similar to other illnesses. The best way to get a diagnosis is by taking a stool sample and looking for Campylobacter bacteria. If you have diarrhea, fever, or abdominal pain, this should be your first step in diagnosis.
What are the complications of Campylobacter? Campylobacter is a foodborne bacterium which is known to cause gastrointestinal infections. It is the second most common bacterium in the United States after Salmonella. The complication of Campylobacter varies from person to person and can range from simple diarrhea to more severe symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, and bloody diarrhea, which may lead to death if not quickly treated.
Campylobacters are bacteria that are commonly found on raw poultry. When ingested, they can cause fever, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Cases of Campylobacter associated with the illness Guillain-Barré Syndrome have also been reported. They can be difficult to diagnose without lab testing or stool cultures because symptoms are similar to other diseases like cholera or salmonella.
Can you get Campylobacter from dogs? Campylobacter is a type of bacteria that can lead to food poisoning, and many people believe that dogs may be the real culprits. The disease occurs when the Campylobacter bacteria in animal feces gets into your mouth. Wouldn't you want to know if your furry friend has this potential? The CDC recommends that any dog who goes near water or dirt should be tested for Campylobacter.
Campylobacter is one of the leading causes of foodborne disease in Canada. While Campylobacter is most commonly associated with poultry, it can actually be transmitted from a variety of sources including infected produce, untreated water, and pets such as dogs. In an attempt to investigate whether Campylobacter could be transferred from a pet to a human, researchers at the University of Guelph collected samples from dogs and their owners and tested them for Campylobacter.
Can Campylobacter cause colitis? Campylobacter can cause colitis. Campylobacters are bacteria that are found in raw, undercooked or unpasteurized poultry, meat and dairy products. The infection is usually diagnosed by testing stool, which can be done up to 2 weeks after the onset of symptoms. Symptoms of the infection include diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramping, fever and rectal urgency.
How do you get rid of Campylobacter naturally? Campylobacter is a species of bacteria that can cause an infection that triggers diarrhea, fever, nausea, and pain. These bacteria are spread through food and water, most often from contaminated sources such as poultry. Many people falsely believe they can get rid of Campylobacter with antibiotics; however, this actually prolongs the illness by strengthening the bacteria within the body.
One of the most common causes of foodborne illness is Campylobacter. It can be contracted through handling raw poultry and other meats, drinking contaminated water, and contact with animals such as cows, sheep, and goats. The bacteria cause diarrhea in humans and is highly contagious. To avoid it in the future, you should wash all surfaces that have come into contact with raw meat or raw poultry immediately after cooking or preparing food.
What part of the body does Campylobacter affect? The bacterium thrives in the intestinal tract of many animals, including birds, cattle, and dogs. Outbreaks related to poultry are most common, but exposure to other types of food or water can also result in infection. Many people develop diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever within 2–5 days of exposure. Most will recover fully within 1 week without treatment.
Every year, millions of people are affected by Campylobacter. These bacteria can cause diarrhea, fever, stomach cramps, vomiting, and bloody stools. Campylobacter is usually transferred to humans by consuming raw or undercooked poultry or unpasteurized milk. It can also be found in untreated water that has been contaminated with the bacteria.
Should I take antibiotics for Campylobacter? Campylobacter is an infection caused by bacteria that is typically transmitted to humans through contaminated poultry or foods. While most people recover without treatment, some people develop life-threatening complications such as anemia and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Campylobacter can be diagnosed via a stool test, but antibiotics are not usually recommended because they are ineffective in relieving the diarrhea associated with the illness.
Can campylobacter lie dormant? Campylobacter is a common cause of infections in humans. The infection has been linked to arthritis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and Reiter's syndrome. Campylobacter can live in the human intestines for months or years after the initial illness, leading to persistence that should be considered in the treatment of diseases that are thought to be associated with it.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that can cause gastroenteritis or inflammation of the digestive tract. Most of the time, recovery only requires a few days, but some people may experience prolonged symptoms. For some people, campylobacter can be what is called “dormant.” This means that they will carry it without any symptoms and can give it to others by not washing their hands after going to the bathroom.
Is campylobacter a parasite? Campylobacter is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes an infectious disease called campylobacteriosis. Campylobacteriosis is an illness in which you get sick from eating food contaminated with the bacteria. Symptoms can include abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or fever and headache. It's usually not serious and most people recover in a few days to a week. Most people who get it recover within a week to 10 days without any problems.
Campylobacter is a microscopic, spiral shaped bacterium that can be found in raw foods. Recently, scientists have begun to question if the bacteria should be classified as a parasite since it does not contain its own genome and contains genes necessary for its replication found in other bacteria.
How can Campylobacter be prevented? Campylobacter is the most common cause of diarrheal illness in the United States. It can be transmitted to humans through contaminated food, water, or contact with live poultry. To prevent Campylobacter, it's important to cook foods thoroughly and avoid contact with animals that are not fully cooked. Campylobacter is a bacterium that's contracted from undercooked or raw chicken. Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, nausea, and vomiting. The best way to prevent Campylobacter is to cook any meat thoroughly before consuming it. All cutting boards and surfaces should be cleaned with hot soapy water after preparing cut meats.
Can Campylobacter cause bowel damage? Campylobacter is a type of bacteria that many people are exposed to in their lives. While it can cause minor symptoms in some patients, in others, it can lead to intestinal tissue damage. The exact reason why the bacteria could cause this type of harm is unknown, but its opportunistic nature suggests that it may have to do with an individual's immune system.
Campylobacter, an organism present in raw or undercooked meat, has been known to cause foodborne illness. The most common symptoms are diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps which can last up to two weeks. More severe cases may include bloody stool, vomiting, and even abdominal pain. According to a new study done by the University of Colorado-Boulder (CU), Campylobacter bacteria could be the cause for necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
Can Campylobacter cause kidney problems? Campylobacter is one of the most common causes of food poisoning in humans. It can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. One possible complication of Campylobacter infection is kidney problems. A recent study has suggested that this may be caused by the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) molecule produced by Campylobacter. The LPS molecule stimulates an immune response in the body, which damages the kidneys.
In conclusion, this article has discussed how the symptoms of Campylobacter vary widely, but generally include abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. The disease is caused by a bacterium that enters the body through contaminated food. The risk factors for acquiring the infection are contact with animals (including farm animals), contact with other people who have been infected, and living in developing countries where this pathogen is endemic.

Kevin Collier is a seasoned health writer at Otchut.com, specializing in over-the-counter medicines, common medical ailments, and general health topics. With a background in healthcare and a passion for making medical information accessible, Kevin aims to empower readers with knowledge to make informed health decisions. When he's not writing, he enjoys researching the latest in health trends and advocating for wellness in his community.