Page Menu
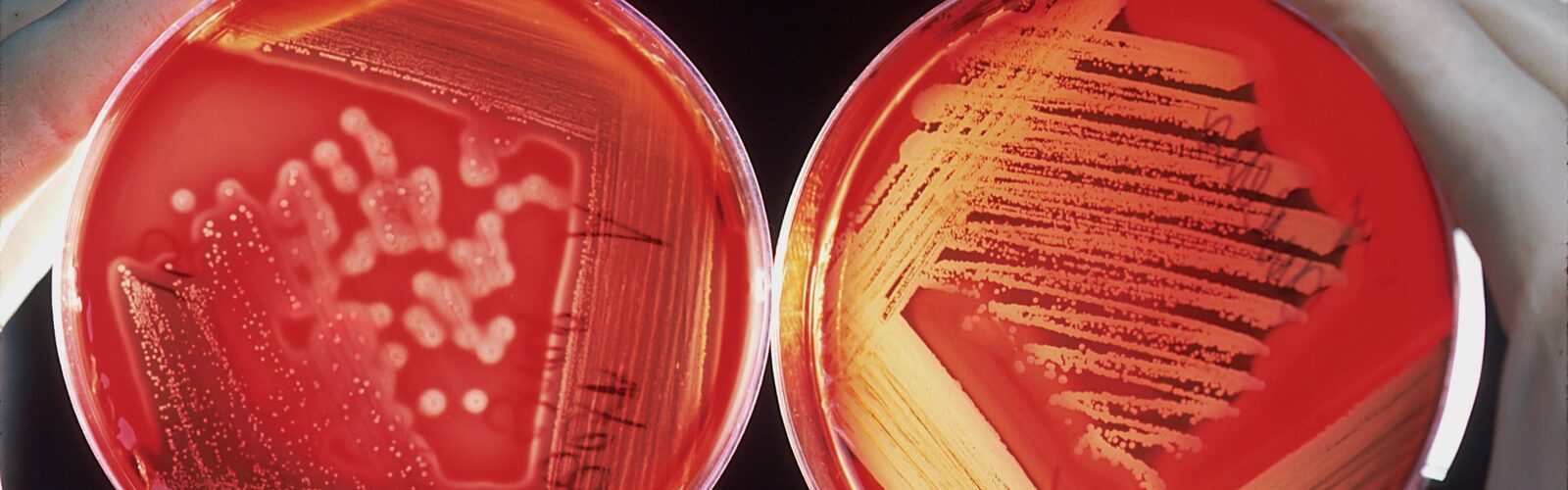
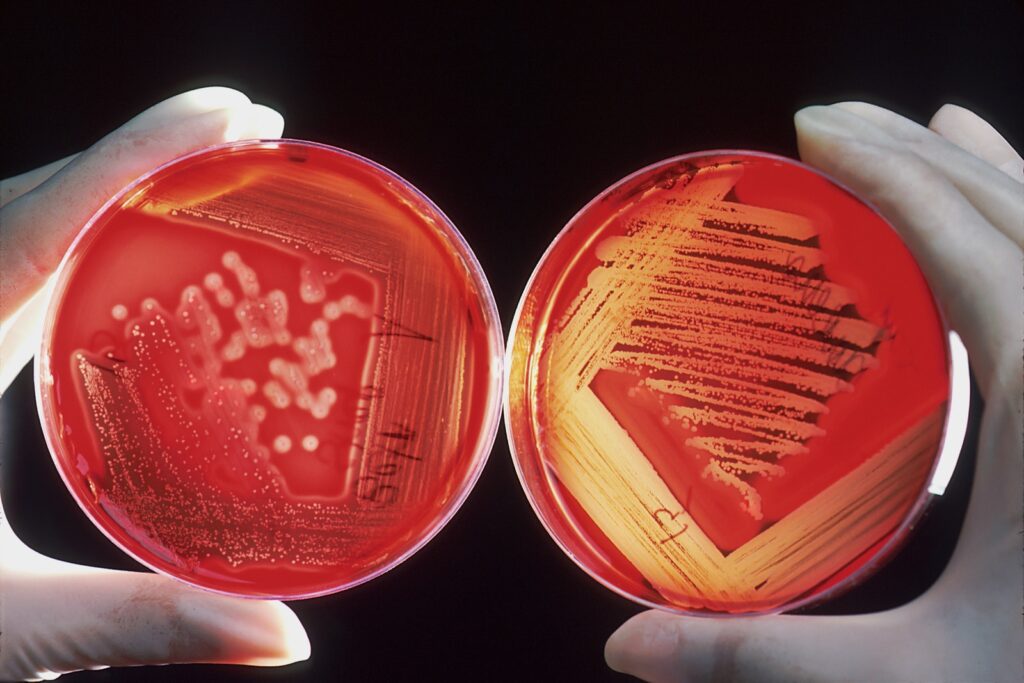
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a type of bacteria that is resistant to many types of antibiotics. MRSA can cause serious health problems if it is not treated quickly. There are several ways to prevent MRSA infection, and the best way to treat it depends on the person's age, health condition, and other factors.
Key Concepts and Top Takeaways
– Recognize symptoms: Look for red, swollen areas on the skin or boils.
– Maintain hygiene: Wash hands regularly to reduce infection risk.
– Keep wounds clean: Clean and cover cuts or abrasions promptly.
– Avoid sharing personal items: Don’t share towels, razors, or clothing.
– Seek medical attention: Consult a doctor if you suspect an MRSA infection.
– Follow treatment plans: Complete prescribed antibiotics even if symptoms improve.
– Monitor for complications: Watch for fever or spreading redness around sores.
– Educate yourself about MRSA: Learn how it spreads and preventive measures.
– Disinfect surfaces frequently: Use antibacterial wipes on commonly touched areas.
– Practice good health habits: Strengthen your immune system with a balanced diet and exercise.
Please Note: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click one of them, we may receive a commission at no extra cost to you. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Many people are unaware of the fact that MRSA can be contracted through various methods. Some of the most common ways that MRSA is contracted are through close contact with someone who is sick, touching an infected surface, or inhaling airborne bacteria. Additionally, MRSA can also be contracted through contact with animals who are carriers of the bacteria. This can include petting an animal that has been in close proximity to a carrier of MRSA, or even handling an animal that has been sick.
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) is a type of superbug that can cause serious health problems. MRSA is becoming more common, and it's possible for anyone to become infected. MRSA can cause skin and respiratory infections, as well as sepsis (a life-threatening condition caused by infection).
If left untreated, MRSA can lead to serious complications, including pneumonia and even death. There are many different ways to get MRSA, and people who are at high risk for infection include those who have conditions that make them more susceptible to infection, such as diabetes or asthma. Anyone can develop MRSA if they're exposed to the bacteria, but there are some risk factors that increase your chances of getting the disease.
Symptoms of MRSA
There are a few key signs that may indicate that you or someone you know is suffering from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA. Some of the more common symptoms include fever, severe skin infections, joint pain and swelling, coughing up blood, and difficulty breathing. If you're experiencing any one of these symptoms and they're not going away with standard antibiotics, it may be worth getting screened for MRSA.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an increasingly common type of bacteria that can cause serious illness in people with weakened immune systems. Elevated body temperature is one indicator of an MRSA infection and can lead to serious health conditions such as pneumonia. Patients who experience fever should contact their healthcare provider for further evaluation.
MRSA, or Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, is a type of bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics. It can cause skin infections, and if the infection is not treated, it can spread to other parts of the body. MRSA skin infections are often a symptom of another disease, and they can be difficult to treat. If you have MRSA skin infection, it's important to get treatment as soon as possible so the infection can be cleared and the risk of spreading the infection reduced.
Joint pain is a common symptom of MRSA infection. The infection can spread to the joints through the bloodstream or through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes. MRSA can also cause inflammation and pain in other parts of the body, such as the lungs, bladder, and kidneys.
The symptoms of MRSA infection vary depending on where the infection is located. In general, people with MRSA infections tend to experience a range of symptoms that can include: fever, chills, fatigue, chest pain, shortness of breath, and trouble breathing. Some people may also experience redness and swelling around the infected area.
If you are experiencing any type of joint pain, be sure to talk to your doctor about it. It's possible that you have MRSA infection and should see a specialist for treatment.
Coughing up blood as a Symptom of MRSA infection is not a common occurrence, but it is possible if the person has contracted the bacteria. The coughing could be spurred on by other symptoms such as fever or shortness of breath. If you are experiencing these symptoms and think you may have contracted MRSA, it is important to seek medical attention.
If you experience difficulty breathing, it may be a sign that you have MRSA. Difficulty breathing may be one of the earliest signs of MRSA infection, and it can often be difficult to detect. If you are experiencing difficulty breathing, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Causes of MRSA
There are many causes of MRSA, but here are the key ones:
-Infected hospitals: People who have MRSA often get it from hospital settings. This includes people who have been in the hospital or treated there, as well as family and friends of people who have been in the hospital. The conditions that make people more likely to get MRSA include being sick and having wounds or surgery. Hospitals can be a high-risk place for catching MRSA, because the bacteria can be spread through contact with infected people or surfaces.
MRSA is particularly dangerous for patients who are already weakened by other conditions, such as diabetes or asthma. People with MRSA often develop a serious infection and may even die if they stay in the hospital long term. In order to protect themselves and others in the hospital setting, it is important to avoid contact with anyone who has an infection and to follow all safety guidelines.
-Infection with other germs: Some people become infected with MRSA while they're healthy, but don't develop any symptoms. Others develop MRSA after getting other infections, such as pneumonia. MRSA is a type of bacteria that can be spread through contact with respiratory secretions, such as saliva or mucus, from an infected person. It can also be spread through contact with wounds or irritated skin. MRSA is most commonly found in hospitals and nursing homes, but it can also be found in schools and other places where people come into close contact with others. MRSA can cause serious infections in the lungs, bones, and other organs.
-Immune system problems: Some people have weakened immune systems due to things like AIDS or cancer treatments. This makes them more likely to get MRSA infections. People who are susceptible to MRSA infections are usually those with a weakened immune system, as well as people who have had surgery or been in the hospital recently.MRSA can also be spread by contact with contaminated surfaces, such as doorknobs, door handles, or countertops. It is important for people who are susceptible to MRSA infections to take steps to protect themselves, such as washing their hands often and avoiding close contact with others who may be infected.
Risk Factors For MRSA
There are many risk factors for developing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). These include: being hospitalized or having surgery; being in a high-risk population, such as the elderly or those with compromised immune systems; using health care services that are not fully effective at preventing the spread of MRSA; and engaging in activities that increase the risk of contact with MRSA, such as working in a hospital or nursing home.
MRSA is a bacterial infection that can be deadly if not treated quickly. There are many risk factors for MRSA, but here are some of the most common:
-Being hospitalized or having surgery: This is the number one risk factor for MRSA. Patients who are hospitalized or have surgery are more likely to develop MRSA than those who don’t.
-Having a weakened immune system: Another big risk factor for MRSA is having a weak immune system. If you have any kind of chronic illness, such as diabetes or asthma, your immune system may be weaker than normal. This makes you more susceptible to getting MRSA if you get it from someone else.
-Having cuts and scrapes: Even tiny cuts and scrapes can allow bacteria to enter your body and cause MRSA infection.
The elderly are at a higher risk for acquiring methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Studies have shown that the elderly are more likely to have skin infections, MRSA infections of the lungs, and bloodstream infections. This is likely due to factors such as poorer wound healing, immobility, and frailty. In addition, many elderly people use multiple medications and may be more susceptible to MRSA infection.
Working in a hospital can be a risk factor for MRSA. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 2% of all MRSA infections occur in healthcare workers. This includes nurses, doctors, and other health care professionals. The risk of getting MRSA increases if you work in an intensive-care unit (ICU), surgery center, or other high-risk area. If you are working in any type of hospital environment, it is important to take the proper precautions to avoid getting MRSA.
Complications From MRSA
MRSA is a problem because it causes many complications. These complications can lead to long-term health problems. Some of the most common complications from MRSA include: pneumonia, bloodstream infections, sepsis, and meningitis. Each of these can be very serious and require medical treatment.
Pneumonia is a common complication from meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In most cases, the pneumonia will resolve on its own, but in some cases it can be more serious and lead to death. MRSA is commonly found on the skin and is often passed from person to person through contact with infected areas. If you are experiencing signs or symptoms of pneumonia, be sure to see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
MRSA is a common type of infection that can occur anywhere in the body. It's caused by the bacteria MRSA, and it can be serious if not treated quickly. MRSA can cause bloodstream infections, which are a very serious complication from the infection. If left untreated, these infections can lead to sepsis (a life-threatening condition caused by overwhelming inflammation), and even death. Treatment for MRSA bloodstream infections typically involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria, along with supportive care to help patients recover as quickly as possible.
Sepsis is a life-threatening complication from MRSA. Sepsis occurs when the body's immune system attacks its own cells, and can lead to organ failure. In most cases, sepsis is caused by an infection with MRSA. However, sepsis can also be caused by other infections or injuries.
MRSA is a type of bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics. When people are infected with MRSA, their immune systems can't fight off the bacteria as easily as they might against other infections. This can cause sepsis, which is an extreme form of the infection.
In severe cases of sepsis, the body can start to lose blood flow to vital organs. This can lead to heart problems, kidney failure, and even death. If you think someone may have sepsis, it's important to get them immediate medical attention.
Meningitis is a serious complication from MRSA infections. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, meningitis is an infection of the meninges, the protective sheath that covers the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms of meningitis may include fever, headache, neck stiffness, and a rash. In more severe cases, symptoms may include confusion, seizures, coma, and death. Meningitis is most often caused by Infections A or C bacteria strains of MRSA.
There are several ways in which MRSA can cause meningitis. One way is through direct contact with the bacteria inside the nose or throat. Another way is when the bacterium spreads from one person to another through close contact (such as during kissing or sharing cups). Finally, MRSA can also spread through contaminated medical equipment such as intravenous lines or surgery tools.
Treatment for MRSA
The most common treatment for MRSA is antibiotics. However, there are other treatments that can be used depending on the type of MRSA and the person's symptoms. A person may also need to take medicines to prevent MRSA from spreading to other parts of their body.
Some of the most common treatments include antibiotics, surgery, and chemotherapy. It is important to choose the right treatment option for your individual situation, as each has its own set of side effects and risks.
Antibiotics are widely used to treat infections, including MRSA. However, antibiotics are not always effective against MRSA because the bacteria can develop resistance. To combat this resistance, doctors often prescribe multiple antibiotics at once or use a combination of antibiotics.
Fortunately, surgery is one of the most effective treatments for MRSA. In fact, it has been shown to be 80-90% effective in treating the infection. However, not all surgeries are appropriate for MRSA patients. Surgery should only be performed if there are no other viable options and the patient is properly screened for MRSA beforehand.
Another important consideration when treating MRSA with surgery is ensuring that the patient receives proper post-operative care. This includes taking antibiotics and wearing a protective mask for at least 14 days after surgery.
Medications and treatments used to treat MRSA include antibiotics, corticosteroids, and chemotherapy. Antibiotics are the first line of defense against MRSA and are effective against most strains of the bacteria. Corticosteroids help relieve inflammation, which is a common side effect of antibiotics. The most common type of chemotherapy used to treat MRSA is doxorubicin. Doxorubicin can kill both cancer cells and MRSA bacteria, making it an important treatment option for patients with this type of infection.
Common Questions About MRSA
How do you get MRSA? MRSA is spread through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes, and it can be difficult to treat because it resists many antibiotics. There are several ways to get MRSA: through contact with an infected person, handling contaminated items, or being exposed to environmental bacteria.
What are the first signs of MRSA? If you're concerned about your health and suspect that you might have contracted Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), here are some of the first signs to watch for: fever, muscle aches, chills, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, blurred vision. These symptoms may indicate that you have an infection and need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Does MRSA ever go away? MRSA is a type of bacteria that can cause a number of infections in the body. However, it is not always easy to treat and sometimes MRSA can be resistant to antibiotics. Despite this, there is evidence that MRSA does eventually go away on its own. In some cases, the infection may clear up completely without any treatment at all. However, most people who get MRSA will experience some form of remission over time.
Is MRSA Contagious? MRSA is a type of bacteria that can be dangerous to people. MRSA is often caused by skin infections, but it can also be spread through contact with objects or surfaces that have been contaminated with the bacteria. MRSA is highly contagious and can easily become spread through the air. If you think you may have contracted MRSA, it is important to get treated as soon as possible.
What does MRSA smell like? MRSA smell different depending on the strain, but typically it has a strong odor. Some people say it smells like cheese or rotten eggs.
What is the best way to control MRSA? There is no one answer to this question as the best way to control MRSA may vary depending on the situation. However, some tips on how to control MRSA include: washing hands frequently, using gloves when handling patients, cleaning patient rooms regularly and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
What internal organ is most affected by MRSA? The most common internal organ that MRSA affects is the lungs, but it can affect any part of the body.
How fast can MRSA spread? MRSA is a highly contagious and dangerous bacteria that can spread rapidly through close physical contact. MRSA can cause serious infection in both adults and children, and can be resistant to many common antibiotics. There is no known cure for MRSA infection, but early diagnosis and treatment is crucial to preventing serious health complications.
How do you know if you have MRSA in your bloodstream? If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should visit a doctor immediately:
-A fever over 104 degrees Fahrenheit
-Severe pain in your chest or abdomen
-Swollen lymph nodes in your neck, armpits, or groin
-Skin lesions that do not heal quickly or spontaneously
If any of these symptoms are present with MRSA skin infection, then it is highly likely that you have MRSA in your bloodstream and should seek medical attention. If at any time during your visit to the doctor you are found to be positive for MRSA, they will administer an antibiotic injection to treat the infection and prevent further spread.
Does MRSA look like a pimple? A person with MRSA may have a number of different symptoms, but one of the most common is a skin lesion that looks like a pimple. In fact, many people mistakenly believe that MRSA is just another type of skin infection. However, MRSA is serious and can lead to death if not treated quickly.
How long is a person contagious with MRSA? Most people are not contagious with MRSA for more than 24 hours after they have been exposed to the bacteria. However, some people can be infected for up to 4 days.
Is MRSA painful? MRSA is a type of bacteria that can cause a lot of pain. MRSA is usually not painful to the touch, but it can be very painful when it's in close contact with other parts of the body. MRSA can also cause a lot of pus to form, and this can be very painful as well.
How do you get rid of boils forever? The best way to prevent boils is by taking simple precautions, like washing your hands often and avoiding contact with people who are sick. If you do get a boil, the best way to treat it is with a topical antibiotic cream or ointment. However, even after treatment, some boils may persist for months or even years. There is no one cure for boils, but there are treatments that can make them less bothersome andeven eliminate them completely.
Is there a vaccine for MRSA? There is currently no vaccine available for MRSA. However, there are a number of treatments available that can help reduce the risk of infection. Some of the most common treatments include antibiotics and MRSA scrubbers.
How often is MRSA fatal? MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) is a bacterial infection that can be deadly if not treated. In the United States, MRSA accounts for about 1% of all hospital-acquired infections but causes up to 25% of all fatal infections. MRSA can be spread through contact with the skin or mucous membranes of someone who is infected, and it often appears in people who have multiple medical problems or are taking multiple medications. The best way to prevent MRSA infection is to avoid coming into close contact with people who are sick.
Are MRSA bumps itchy? The bumps commonly referred to as MRSA bumps are actually clusters of bacteria that can cause intense itching. MRSA is most commonly found on the skin of the face and neck, but it can also be found in other areas of the body. If you have MRSA bumps, it's important to seek medical attention as soon as possible as the bumps may indicate a more serious infection.
Do patients with MRSA need to be isolated? If it is not treated, MRSA can cause serious health problems. Some people might think that patients with MRSA should be isolated, but this is not always necessary. There are many ways to prevent MRSA from spreading and it is important to take the time to find out which approach is best for each individual patient.
How can I treat MRSA at home? There are a few ways to treat MRSA at home. Some people might use antibiotics or antiseptics to fight the bacteria, while others might use natural remedies such as garlic or honey. Additionally, people can try to keep their environment clean and avoid touching their eyes, noses, or mouth.
Does MRSA affect the brain? MRSA is a type of bacteria that can cause infections in the blood and other organs. Some studies have suggested that MRSA can affect the brain, but more research is needed to confirm this. If MRSA affects the brain, it could lead to serious complications such as meningitis or even death. However, until more research is conducted, it’s difficult to say for sure what role MRSA plays in the brain.
What happens if you test positive for MRSA? If you test positive for MRSA, there are a few things that can happen. If the MRSA is on your skin or in your nose or mouth, it can cause infection and may need to be treated with antibiotics. If the MRSA is in your airways (the air passages inside your lungs), it can cause pneumonia, a serious lung infection. If the MRSA is in your blood, it can cause sepsis (a life-threatening condition caused by infection), and if untreated, may lead to death.
Can you get MRSA from poor hygiene? Poor hygiene is one of the most common causes of MRSA. This bacteria can be spread through contact with skin, blood, saliva or mucus from an infected person. It's also possible to get MRSA from contaminated surfaces. Be sure to keep your hands clean and avoid contact with sick people. If you do get MRSA, get treatment as soon as possible.
Does MRSA cause kidney failure? In some cases, MRSA can cause kidney failure. Studies have shown that people who have MRSA infections are more likely to develop kidney failure than people who don’t have MRSA infections. However, the cause of kidney failure caused by MRSA is still not clear.
In conclusion, MRSA symptoms can be difficult to diagnose and may often be mistaken for other types of infections. It is important to be aware of the causes and risk factors associated with MRSA in order to reduce your risk of developing a serious infection. If you are experiencing any symptoms of MRSA, it is important to seek medical attention right away.

Kevin Collier is a seasoned health writer at Otchut.com, specializing in over-the-counter medicines, common medical ailments, and general health topics. With a background in healthcare and a passion for making medical information accessible, Kevin aims to empower readers with knowledge to make informed health decisions. When he's not writing, he enjoys researching the latest in health trends and advocating for wellness in his community.