Page Menu
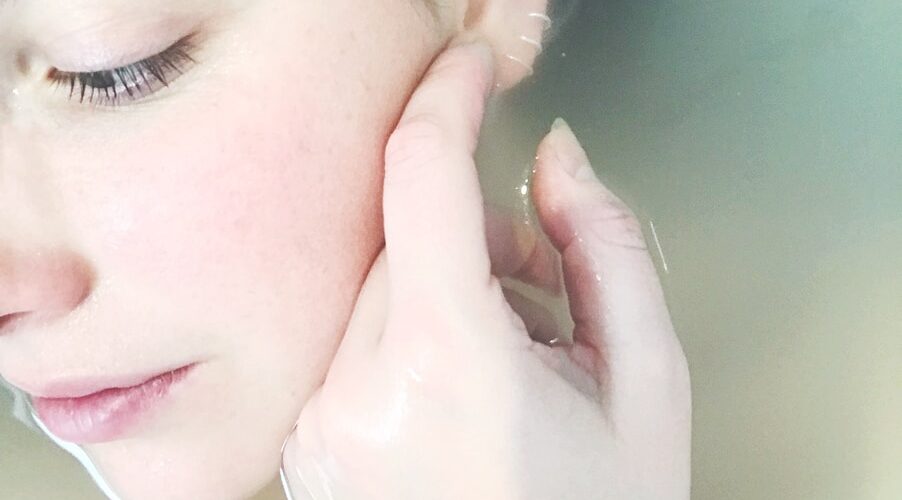
Dermatillomania, also known as “skin picking disorder,” is a mental health condition characterized by repetitive and excessive skin picking. Dermatillomania causes and symptoms may include skin lesions, scars, infection or inflammation on the skin, and sometimes even disabilities that can lead to social isolation. Dermatillomania treatment is available with medication such as antidepressants and antianxiety medicine.
Key Concepts and Top Takeaways
– Recognize the behavior: Identify when and why you engage in skin picking.
– Keep a journal: Track triggers and emotions associated with skin picking episodes.
– Set achievable goals: Aim to reduce picking gradually rather than stopping abruptly.
– Use barriers: Wear gloves or bandages to limit access to your skin.
– Find alternative activities: Engage in stress-relief practices like fidget toys or art.
– Practice mindfulness: Incorporate meditation or deep breathing exercises into your routine.
– Seek support: Talk to friends, family, or support groups about your struggles.
– Consult a therapist: Consider cognitive-behavioral therapy for professional guidance.
– Explore OTC treatments: Use soothing creams or moisturizers to promote healing.
– Celebrate progress: Acknowledge small victories in reducing skin picking behavior.
Please Note: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click one of them, we may receive a commission at no extra cost to you. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

This type of obsessive-compulsive disorder may cause the sufferer to feel a sense of relief or pleasure that temporarily distracts from any tension or anxiety they may be feeling deep within themselves. It can cause significant distress and impairment in everyday life and lead to infections, scarring, and other complications.
Some may try to pick at scabs or open wounds, while others may focus on the slightest of skin imperfections, resulting in bleeding and infection. Sufferers of dermatillomania may also scratch or rub themselves, leaving marks all over their bodies. Some speculate that dermatillomania is a form of self-harm, either as a way to relieve anxiety or as a way to feel something other than pain. The condition is characterized by the inability to control urges to pick at one's own skin until it bleeds.
Dermatillomania is an obsessive-compulsive disorder, characterized by the sufferer's need to pick at her skin. This can be done on any part of the body, though it most often occurs on the face, underarms, hands or feet.
Causes of Dermatillomania
If you suffer from Dermatillomania, the urge to pick your skin is a distinct sensation that can overcome you at any time. The condition affects a high percentage of adults and children in the United States. There are many reasons for this disorder including genetics, anxiety, obsessive compulsive disorder, and depression.
Dermatillomania, also known as skin picking disorder, is a mental disorder in which people are compelled to pick at their skin. It has been observed to occur most often in people who are emotionally vulnerable or have experienced some sort of trauma. Dermatillomania is not curable, but it can be controlled with medication or therapy.
Before understanding why genetics can cause Dermatillomania, it is important to understand what the disorder entails. People who suffer from Dermatillomania tend to pick at their skin for reasons such as reducing anxiety, stress, or boredom. It is not uncommon for this behavior to be so severe that people develop wounds on their skin or severe bouts of infections. Genetic research has shown that there are many genes responsible for making someone more likely to develop dermatillomania.
Some people might not see the connection between genetics and dermatillomania, but for those who suffer from this disorder, it is clear that genetics are a contributing factor. When there is a genetic predisposition to developing obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD), there's often an increased risk of developing dermatillomania. Children with at-risk genes are more likely to develop OCD than normal children, which means they're also more likely to develop dermatillomania.
Experts are unsure of the exact cause of Dermatillomania, but stress, anxiety, and genetics are commonly hypothesized as major contributing factors. Dermatillomania, also known as Dermatophagia, is a disorder in which one obsesses over the perceived appearance of their skin. Research has now begun to show that anxiety may play a role in the development of this disorder. Anxiety is an emotion that often leads to behavioral changes, with the most notable being avoidance behaviors.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a type of anxiety disorder. It can be characterized by unwanted, intrusive thoughts that are accompanied by feelings of worry or terror, repetitive behaviors that are designed to suppress the obsessive thoughts, and avoidance of people or places that remind one of their obsession. OCD can take many forms.
Dermatillomania, also known as skin picking disorder, is a condition characterized by the obsessive desire to pick at your skin. Individuals with Dermatillomania often feel compelled to pick at their skin for relief from stress or anxiety. Sometimes they have an urge to do this just because of low self-esteem and poor body image. Dermatillomania can affect the skin on any part of the body but is most common on the face or hands.
Dermatillomania, or skin picking disorder, is a little-known disorder that affects up to 10% of the population. Those with this condition will often pick at their own skin until they bleed. This can lead to disfigurement and infection, which can reduce self-esteem and destroy relationships.
Symptoms of Dermatillomania
Dermatillomania, also known as the Skin Picking Disorder, is a psychological disorder that affects nearly 2% of Americans. Sufferers will typically pick at their skin until they form a sore and bleed. This behavior usually starts in the teenage years and can last for decades if not properly treated. Dermatillomania is a diagnosis made by a dermatologist based on observation and clinical judgment, with no blood tests or imaging needed for confirmation.
People with this disorder tend to spend hours at a time chewing on, rubbing, and picking at their skin. This may lead to scabs, sores, bleeding, and infection. Dermatillomania sufferers find that they can alleviate their anxiety or stress during the act of skin picking, despite the physical damage caused by the behavior.
Skin lesions are a common symptom of Dermatillomania, which is the compulsive need to pick at one's skin. Usually, these sores do not bleed and can be found on any part of the body that can be reached by the sufferer. The picking often takes place during periods of boredom or frustration with oneself or in response to feelings of depression, anger, or anxiety.
Many people in this world suffer from a mental disorder known as Dermatillomania, in which the individual compulsively and repetitively picks at their skin. The most common type is Pruritus (a term for excessive itching) with an estimated 2-3% of the population suffering from it. One of the most devastating side effects is that it leaves wounds such as scars on your skin that can affect your confidence and self-esteem.
Dermatillomania is a chronic condition in which an individual compulsively picks at their skin, creating noticeable scabs and scars. The picking often leaves the skin raw and sometimes bleeding, leaving a pile of skin that can be seen on the person's clothes or in his or her hands. The disorder is known by many different names, including dermatitis manica rubra – excessive skin-picking – and excoriation disorder.
In some cases, the disorder may be triggered by an emotional event or by a physical condition. Dermatillomania can cause severe emotional distress and problems in other aspects of daily life, making it a difficult disorder to manage on one's own.
Sufferers of dermatillomania are often unaware of their actions, yet the repetitive nature of the behavior can lead to physical damage and emotional distress. Though many sufferers are able to hide their symptoms successfully, there are still many who must live with constant embarrassment and shame.
A person may do this because it produces a feeling of relief or release, or because they are trying to deal with stress. It can be difficult to identify dermatillomania in oneself because it happens so often and isn't always noticeable to others around us. Inflammation on the skin may be an indicator that someone is suffering from dermatillomania.
Treatment for Dermatillomania
Treatment for Dermatillomania can vary depending on the severity of the picking; some people may benefit from talk therapy, while others need more support and guidance.
Dermatillomania can be caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, environmental factors, or genetics, so it is important for sufferers to consult with a mental health professional before starting any self-treatment.
A new study found a way to help people with dermatillomania. It is a disorder in which people can't stop picking at their skin.
In the past, some doctors have prescribed medications to try to stop the urge to pick, but these drugs cause uncomfortable side effects and may even increase the urge to pick. The new study examined how an experimental procedure called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) can reduce urges.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a therapy that has been used to treat individuals who suffer from addiction. The therapy uses electromagnetic induction of electric currents in order to stimulate specific areas of the brain, which causes changes in various neurotransmitters and subsequently behavior. TMS has been successful in reducing urges for alcohol, cocaine, heroin use, smoking, gambling, and overeating.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a technique that uses magnetic pulses to the brain to stimulate the nerve cells and alter their activity. It has been shown to reduce urges associated with addiction, as well as lessening impulsivity. It is noninvasive and painless, making it an attractive alternative for people who are struggling without success with traditional methods of treatment.
Treatment options include medication, therapy, lifestyle changes, and dermatillomania support groups. This article will focus on treatments available without a prescription.
This is a list of things that can be done in order to manage Dermatillomania through the use of OTC treatments.
1) It is suggested to try ice packs, which can be found at any pharmacy, for about 15 minutes a day.
2) Keeping the hands busy by doing activities such as knitting or playing with play dough is also a suggestion from an article found on Psych Central.
There are treatments for Dermatillomania including cognitive behavioral therapy and medication, but many individuals with Dermatillomania find it difficult to quit because of the mental and physical cravings.
Common Questions About Dermatillomania
Those with this disorder sometimes pick at their skin to relieve tension and anxiety, similar to someone who bites their nails. Common questions people may have range from what it feels like to pick your skin to the difference between dermatillomania and track marks.
This disorder can be both physically and mentally painful for those who deal with it. There are many common questions, such as “What causes dermatillomania?” and “How do I know if I have dermatillomania?”, but often people don't know where to go or who to talk to in order to get answers.
Is dermatillomania a mental illness? Dermatillomania is the obsessive compulsive disorder involving picking at one’s skin. It is usually not something that can be treated as a standalone issue and often co-occurs with other mental illnesses such as anxiety, depression, and OCD. Dermatillomania can be treated with CBT.
Is skin picking a symptom of anxiety? People who struggle with anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder are more likely to struggle with skin picking than those who do not suffer from these conditions. Skin picking, also known as dermatillomania, can arise in many different situations and be habitual for some people. For example, one might pick at their skin after they feel pressured by work deadlines or while watching television.
There is a growing concern among mental health professionals and patients alike about the rise in Skin Picking Disorder, also known as Excoriation Disorder, according to a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. The study found that some people suffering from this disorder may be suffering from co-morbid anxiety, OCD, or depression.
Why does picking scabs feel good? Picking scabs is an unfortunate instinctive action that many of us have probably done at one point in our lives. The urge to pick at a scab is thought to have roots in the ancient practice of bloodletting to cure illness. Although, research by psychologist Dr. Rachel Vreeman has linked this habit in children with obsessive-compulsive behavior when they are young.
There are many reasons why picking scabs can feel good. For some people, picking might relieve their anxiety or stress. For others, the satisfaction of removing something that is embedded in the skin can be rewarding. Lastly, for some people, relief from itching is a reason they might pick at scabs.
Does putting Vaseline on a scab help? Many people put Vaseline on a scab to help it heal faster, but the truth is that there's no evidence that this actually helps. In fact, experts say that putting Vaseline on a scab can actually slow down healing, as the petroleum jelly creates a moist environment where bacteria thrive.
There is no scientific evidence to support the idea that Vaseline helps scabs heal better. The myth started back in 1879 when it was advised by a doctor to place petroleum jelly on a healing cut. The doctor, Dr. W. T. Gordan, said he had found this tip in an old family medical guide that recommended “anointing cuts or abrasions with an ointment of petroleum jelly.
How do I know if I have dermatillomania? Do you compulsively pick at your skin? Do you worry about the size, shape, and condition of your skin? Are you afraid that you might have a blemish or scar, when in reality you don't? If so, it might be possible that you have dermatillomania. Dermatillomania, also known as compulsive skin picking, is an impulse disorder where people obsessively pick at their skin to relieve tension or a “high” feeling that it provides.
A common misconception is that dermatillomania, or skin picking, is the same thing as obsessive-compulsive disorder or OCD. It is not. While it can be very difficult to stop picking once the behavior has begun, it does not have to be a lifelong struggle. Dermatillomania can be treated by identifying triggers and working with a therapist who specializes in cognitive behavioral therapy.
How do you stop dermatillomania? People with dermatillomania are obsessed with picking at their skin. They do not know when to stop, and it can be emotionally draining for them and those around them. The first step to overcoming the habit is being aware of the problem. We should all be mindful of our own behaviors to avoid this disorder. There are other ways besides surgery or medications that people have found helpful in combating dermatillomania.
Is skin picking a bad habit? Skin picking, also known as Dermatillomania, is a behavioral disorder that causes sufferers to compulsively scratch, pick, or dig at their skin. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including anxiety and boredom. While it may be hard for many people to understand the compulsion to pick at one's own skin, it is important not to judge those who suffer from the condition.
What happens if you pick a scab over and over? People have developed scabs for a variety of reasons. Some may pick at a cut out of boredom, some out of addiction, and others in an attempt to ward off infection. Scabs are not just spots that need to be covered up or hidden in your social life. They are part of the healing process. Picking at them is counterproductive and can leave you with unwanted scars.
Can you have dermatillomania without OCD? Some people with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) do not have another related disorder, such as depression or anxiety. However, some people who have dermatillomania, a form of obsessive compulsive disorder, also suffer from other disorders.
Research has shown that many people with OCD also have a mood disorder in addition to their OCD. In some cases, the onset of OCD may be linked to the onset of the mood condition.
Many people live with dermatillomania without OCD. Dermatillomania is an obsessive compulsive disorder, and often people who have it do not have OCD. Dermatillomania, which is commonly called skin picking, can affect the face and body and often leads to serious skin problems and infections. Sometimes dermatillomania is considered a form of self-harm because it becomes an addiction for some people.
Why does scratching scalp feel good? Scratching your scalp feels good because the act of scratching stimulates nerve endings in the skin. When you scratch an itch on your arm, the nails of your fingers are pressing against nerve endings in the arm's surface, causing a pleasant sensation. Your scalp contains these same nerve endings, which are stimulated by scratching to provide relief for an itchy scalp.
Will my hair grow back after picking my scalp? Most scabs will heal over time, but if the scalp is picked so aggressively that the skin has been removed, it could take a long time for all the dead skin to build up and for hair to grow. If the scalp is not allowed to rest and/or there is not enough protein in the diet, then there is a higher chance that bald patches may appear and/or existing hair may become dry and brittle.
Often times, when someone is experiencing hair loss, they will try to pick at their scalp in order to get more hair. This can be detrimental to the health of their hair and make them more susceptible to having bald patches on their head. It's important for people who are feeling insecure about their hair that they don't pick at their head or pull out strands.
Why does Adderall make me pick my skin? You might not realize it, but some people develop dermatillomania as a side effect of taking Adderall for ADHD.
Adderall is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for adults and children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Although it is not the only treatment available for this condition, Adderall can be highly effective in treating ADHD and related symptoms. It also carries a low risk of serious side effects and abuse potential.
Is skin picking a symptom of schizophrenia? There is some speculation that skin picking could be a sign of schizophrenia, but more research is needed to confirm this theory. Skin picking can lead to infections and scarring on the skin, which can be a detriment for sufferers. One study has shown that people with an anxiety disorder may have a higher risk for developing a skin picking disorder, which would suggest it might be an uncontrollable urge associated with anxiety.
Can dermatillomania be cured? This is a question that is answered by many dermatologists and scholars. Some say yes, some say no. Others would even debate the definition of the term “cure.” Can it be reduced or slowed down as a result of therapies such as cognitive behavior therapy? Yes, but we cannot guarantee that we will never pick again.
This question is difficult to answer, but there are ways to deal with this condition. One of the best ways to cope with dermatillomania is by using the Emotional Freedom Technique (EFT). EFT is a psychological approach that can help one release negative emotions and thoughts while acknowledging positive ones. It works by stimulating acupuncture points so that energy flow will be restored in the body.
In conclusion, dermatillomania is a disorder that can cause great distress in the lives of those who suffer from it. Fortunately, with the right treatments and care, sufferers can find relief in their lives.
People suffering from dermatillomania may want to try over the counter treatments such as benzocaine cream, mineral oil, or ointments with lidocaine in them to help with some of their symptoms.

Kevin Collier is a seasoned health writer at Otchut.com, specializing in over-the-counter medicines, common medical ailments, and general health topics. With a background in healthcare and a passion for making medical information accessible, Kevin aims to empower readers with knowledge to make informed health decisions. When he's not writing, he enjoys researching the latest in health trends and advocating for wellness in his community.